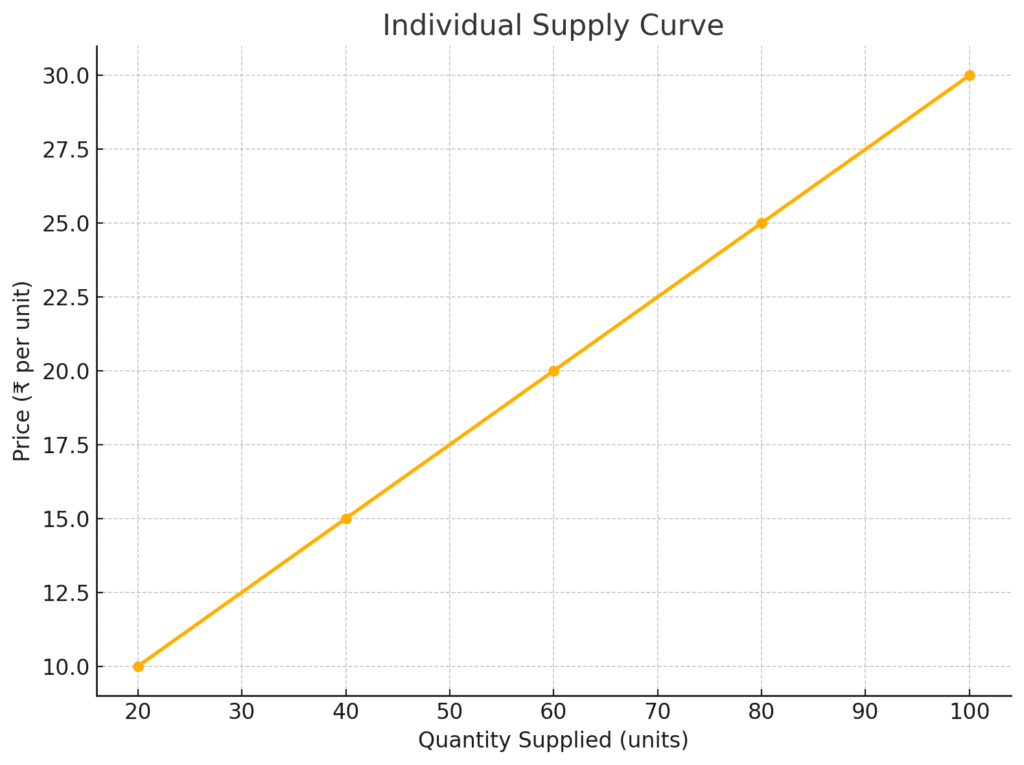In this article you’ll learn about Supply Curve Shifts.
1. Movement and Shift In Supply Curve
Understanding supply curve behavior is crucial to analyzing how producers respond to different market conditions. Let’s explore the two major concepts: movement along the curve and shifts of the curve.
1.1 Movement in Supply Curve
A movement along the supply curve occurs when the price of the good changes, and this causes a change in the quantity supplied — but the supply curve itself does not move.
- Price increase → movement upward (expansion)
- Price decrease → movement downward (contraction)
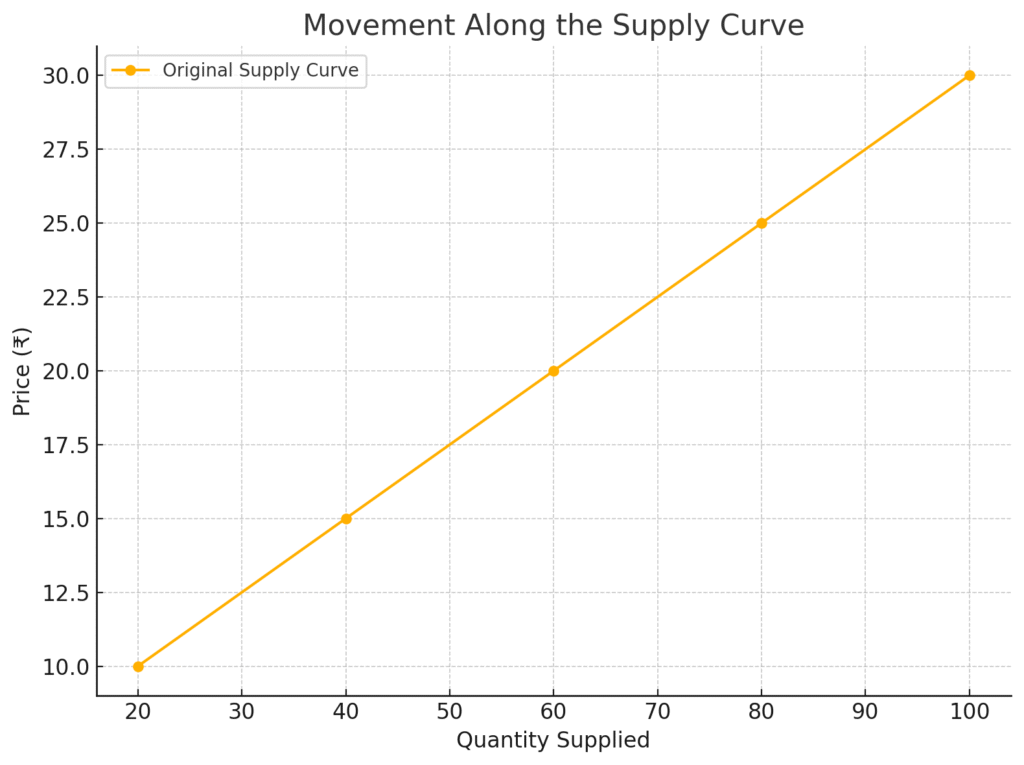
Here is the graph showing Movement Along the Supply Curve – representing expansion and contraction of supply due to price changes.
1.2 Shift in Supply Curve
A shift in the supply curve occurs when the quantity supplied changes at the same price due to factors other than price, such as:
- Changes in technology
- Government policy
- Input prices
- Number of sellers
A rightward shift indicates more supply at the same price (increase in supply).
A leftward shift indicates less supply at the same price (decrease in supply).
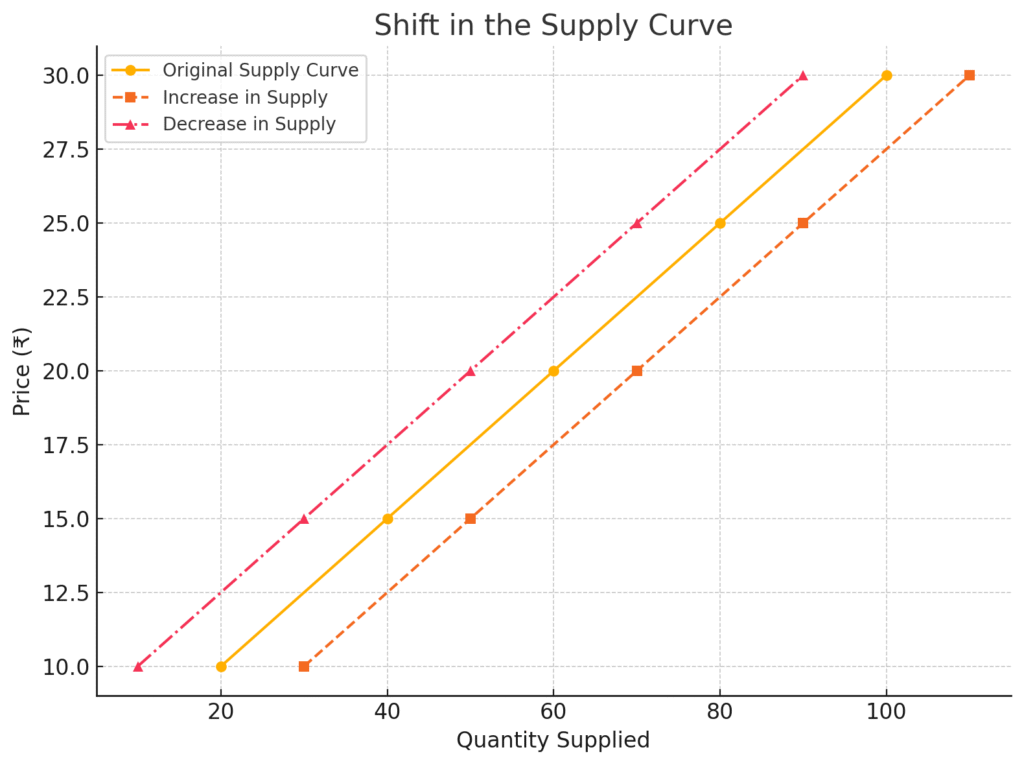
2. Shifts and Movement along Supply Curve
Let’s now break it down further into two categories:
2.1 Expansion and Contraction of Supply
These are movements along the same supply curve, caused by price changes only.
2.1.1 Expansion or Extension of Supply
Occurs when price increases and the seller is willing to supply more.
Example:
Price increases from ₹10 to ₹15
→ Quantity supplied increases from 20 to 40 units
2.1.2 Contraction of Supply
Occurs when price decreases and the seller is willing to supply less.
Example:
Price drops from ₹30 to ₹20
→ Quantity supplied drops from 100 to 60 units
2.2 Increase and Decrease In Supply
These are shifts of the supply curve, not movements along it.
2.2.1 Increase In Supply
Occurs when more quantity is supplied at the same price, usually due to better technology, subsidies, or lower input costs.
→Supply curve shifts right.
2.2.2 Decrease In Supply
Occurs when less quantity is supplied at the same price, often due to supply chain issues, high taxes, or natural calamities.
→Supply curve shifts left.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between movement and shift in a supply curve helps interpret supply-side behavior more accurately in economics. Whether you’re analyzing a small shop or an entire market, this concept is key to making informed economic decisions.